CURIOX APPLICATIONS
COVID-19 & INFECTIOUS DISEASE
Reduce aerosol generation from infectious samples to improve biosafety.
- Home
- Applications _ Covid-19 & Infectious disease
Overview
CHANGE THE WAY YOU PROCESS CELLS TO GET RELIABLY CONSISTENT DATA.
The World Health Organization Laboratory guidance for research on the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV2 states, “all technical procedures should be performed in a way that minimizes the generation of aerosols and droplets.”
| Table 1. Risk prioritization of selected routine laboratory tasks | ||||
| Task or activity | Exposure risk | |||
| Potential hazard | Likelihood | Consequence | Risk rating | |
| Subculturing blood culture bottle | Needle stick — percutaneous inoculation | Likely | Infection; medical treatment | High |
| Aerosols — inhalation | Moderate | Infection; medical treatment | Medium | |
| Splash — direct contact with mucous membranes | Moderate | Infection; medical treatment | High | |
| Centrifugation | Aerosols — inhalation | Likely | Infection; medical treatment | High |
| Performing Gram stain | Aerosols from flaming slides | Moderate | Colonization; infection | Moderate |
| Preparing AFB smear only | Aerosols from sputum or slide preparation | Likely | Illness; medical treatment; disease | High |
| Performing catalase testing | Aerosols — mucous membrane exposure | Unlikely | Colonization; infection | Low |
| AFB culture work-up | Aerosols — inhalation | Likely | Illness; medical treatment; disease | High |
| Abbreviation: AFB = acid-fast bacillus. | ||||
Curiox Biosystems introduces a new, safer method for preparing potentially or known infectious blood samples for immune cell profiling without a centrifuge, eliminating aerosolization of potentially infectious samples. The method combines a new configuration of the Laminar Wash HT2000 system packaged with STEMCELL Technologies EasySep RBC depletion reagent to enable blood sample processing within a biosafety cabinet from start to finish.
This natural and gentle cell prep method relying on Laminar Wash technology improves viability, retention, and staining resolution of rare and sensitive immune cell subsets known to play crucial roles in the immune response against COVID-19 infections, like monocytes and neutrophils. Improvements in data quality due to reduced stress are evident even on fragile cells resulting from harsh methods such as red blood cell lysis that relies upon repeated centrifugation steps.
“The Laminar Washer is safer than flicking [minimizing exposure to infectious materials] and requires less space than centrifuges.”
Blanca Ponce-Ngo, Montefiore Medical Center
Traditional centrifugation
VS
Laminar flow technology
Comparison of an immuno-staining workflow for the preparation of a single cell suspension for flow cytometry analysis. Laminar Wash technology is equally effective in washing but without the use of a centrifuge.
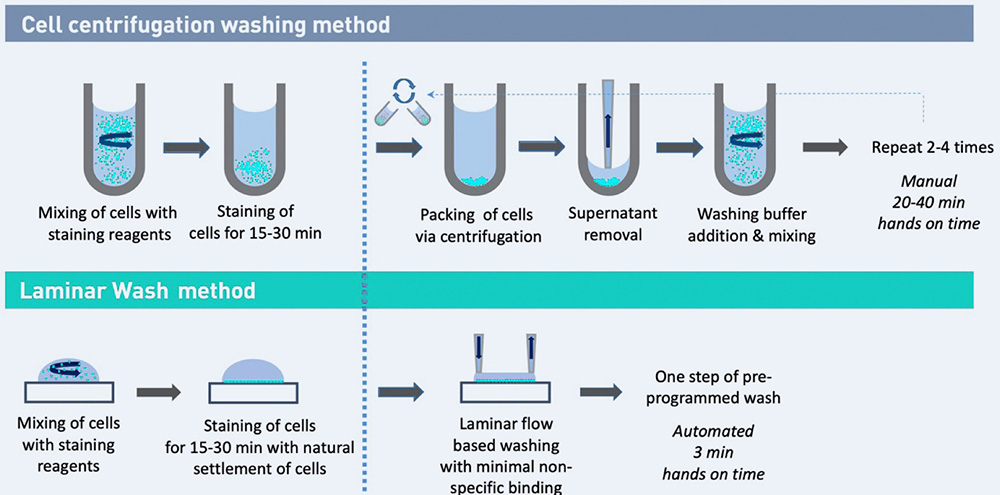
Benefits
Laminar wash for single cell sequencing & proteogenomics
- Enhancing workflow safety through biosafety cabinet containment
- Reducing aerosol production from samples
- Reducing debris, background, and instrument clogging
- Improving resolution and stain index
Featured Resource
Severe COVID-19 infection is associated with aberrant cytokine production by infected lung epithelial cells rather than by systemic immune dysfunction

Scientific Data
Data using the laminar wash system
LW is Gentle on Both Neutrophils and Monocytes
Laminar Wash technology was compared to centrifugation protocols in a 16-color immune profiling panel using 100μL of whole human blood. One-step washing using Laminar Wash minimized cell perturbations compared to multiple centrifugation steps, increasing retention of both the monocyte and neutrophil populations.
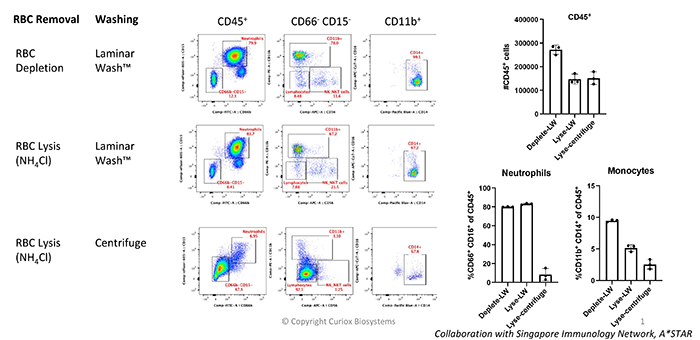
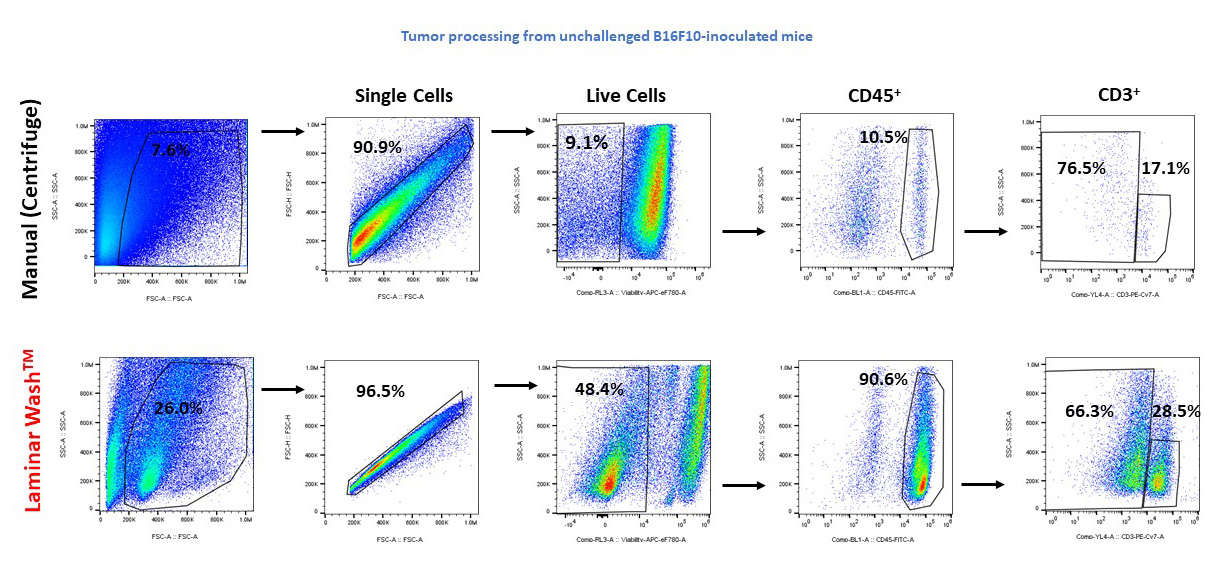
Better Debris Removal and Cell Retention
When performing cell dissociation in tumor-bearing tissues, tissue debris and enzymatic-induced fragments are primary factors affecting recovery of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). For more invasive and immunologically challenging models, like B16F10-inoculated mice, recovery of limited numbers of TILs hinders accurate characterization. Here, Laminar Wash technology was compared to conventional methods for preparing an unchallenged mouse sample containing ~1,000,000 tumor infiltrate cells. Laminar Wash improved viable cell count and reduced debris formation. The cleaner sample preparation increased lymphocyte recovery up to 90.6%, compared to 10.5% for the centrifuge.
Data adapted from the Curiox Biosystems webinar by Dr. Christoph S. Eberle, Discovery Research Services at Charles River Laboratories, Worcester, MA
RELATED PRODUCTS AND ACCESSORIES
Curiox Laminar Wash
LAMINAR WASH™ HT2000 SYSTEM
Achieve higher throughputs and cleaner data with our 96-well laminar washing system.

Curiox Laminar Wash Auto
LAMINAR WASH™ AUTO 1000 SYSTEM
Accelerate high-throughput flow and mass cytometry workflows with fully automated sample preparation.


